Human Pose Estimation
The Human Pose Estimation node leverages Human Pose Estimation (HPE) to identify and classify human joints in real time. This technique captures a set of coordinates for each major joint (like the arms, head, and trunk), referred to as keypoints, which help determine a person’s posture. By tracking these keypoints, the Human Pose Estimation node enables the creation of responsive animations and special effects that adapt to specific poses.
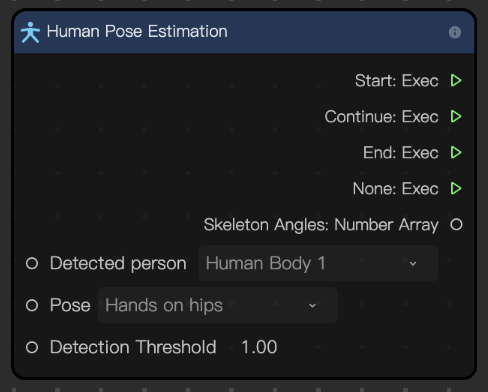
Input
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Detect | String | The body to detect. "Body 1" represents the first person to appear in the scene and "Body 2" represents the second. |
| Pose | String | The pose to be detected |
| Detection Threshold | Number | Determines how strict the detection logic is. The higher the number, the stricter the logic. The default value is 1. |
Output
| Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Start | Exec | Executes the next node when the specified pose is detected |
| Continue | Exec | Executes the next node continuously as long as the pose is detected |
| End | Exec | Executes the next node when the pose is no longer detected |
| None | Exec | Executes the next node if the pose isn't detected in a frame |
| Skeleton Angles | Array | Outputs the angles between bones in order. Multiple bones can be combined to manually calculate the pose. |
Pose Estimation Model
Pose estimation can be performed using the contour-based model (planar model).
This model represents the body in two dimensions, using outlines to capture the approximate shape and width of the body, trunk, and limbs. Instead of tracking individual joints, it depicts body parts through contour boundaries and rectangles, providing a simplified yet effective representation of the human form. This model is particularly useful for applications that require an understanding of body shape and silhouette rather than precise joint movement.
Example Use Cases
The Human Pose Estimation node can be used in a visual scripting graph to trigger various interactive effects, including:
- Squat detection: Monitor the relative positions of the hip, knee, and ankle keypoints to detect when the user is squatting.
- Gesture-based animations: Track hand and arm positions to trigger animations or interactive responses based on specific gestures
- Dance pose recognition: Track different body parts to identify or analyze dance poses